Plant Tissues
Plant Tissues: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Xylem, Vessels, Parenchyma, Phloem, Plant Tissues, Sclerenchyma, Collenchyma, Permanent Tissues, Apical Meristems, Tracheids, Meristems, Sieve Elements, Simple Permanent Tissues and, Complex Permanent Tissues
Important Questions on Plant Tissues
Observe the given structure of phloem tissue in a plant, and choose the name of part X.
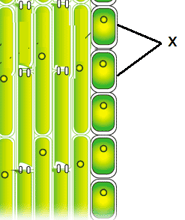
Phloem fibre is an element of xylem tissue.
_____transports food from leaves to other parts of the plant.
_____parenchyma are a type of tissues having vascular functions which consists of living cells having thin cell walls.
_____ transports water and minerals from roots to leaves of the plants.
_____ is the example of protective tissue in the plants.
_____cells are present in the stems, veins and midribs of leaves.
_____ present in the parenchyma (aerenchyma) of aquatic plants help the plant to maintain buoyancy in water. (Large air cavities/Large lignin cavities)
_____ is the type of parenchyma, which contains chlorophyll.
_____is the basic packing tissue of a plant.
_____is the process by which cells divide meristematically to take a permenent shape, size and function.
_____ is the type of meristem tissue which is present at growing tips of stem and roots.
_____tissue siruated at growing tips of regions of plant is responsible for growth of plant.
_____tissue is mainly found in soft parts of the plant such as roots, stem, leaves.
Cells of this tissue is capable of dividing and re-dividing. Identify the tissue.
Which category of tissues does xylem and phloem belong to?
